Students and academics from the University of Melbourne joined forces with selected consultants from industry and CSIRO’s property sustainability team to explore the question of net zero laboratory design. The university’s Brendon McNiven, Dominik Holzer and Lu Aye, F.AIRAH elaborate.
By Sean McGowan
Laboratories are key facilities in the frontline research work society needs to answer many of the world’s most pressing problems. The strict requirements laboratories impose on indoor environment controls – along with the strong focus the experiments being undertaken attracts – often means the potentially negative effects associated with the construction and operation of laboratory buildings are overlooked.
As Australia’s pre-eminent research organisation, CSIRO is keen to address this. Carrying out a good deal of research into climate change themselves, CSIRO has ambitious targets to reach net zero greenhouse emissions in place, as an organisation, by 2030.
With this target in mind, in 2021 students and academics from the University of Melbourne joined forces with selected consultants from industry and CSIRO’s property sustainability team to explore the question of net zero laboratory design. The work was undertaken as a part of the i-Hub affordable heating and cooling program, an innovation hub initiated by AIRAH, and funded by Australia’s renewable energy agency, ARENA.
The premise of the studios was to marry architecture and engineering more closely together at the early design stage, to generate building solutions that excel both in their architectural outcomes as well as their technical performance. This concept is known as “integrated design’.
“The potentially negative effects associated with the construction and operation of laboratory buildings are overlooked”
The Integrated Design Studios (IDSs) process
The resulting integrated design studio (IDS), that was set up developed a brief for what was considered a typical CSIRO “PC2” laboratory building. This was then used as a case study on which masters-level student designers (both architects and engineers in the same studio), prepared building designs. Design outcomes were then vetted by consultants for feasibility in reducing carbon outcomes.
The studio found reductions of approximately 50 percent in the business-as-usual operational energy demands from grid were possible. This was achieved through the culmination of demand reductions from the introduction of passive design measures and energy-efficient specifications (18 per cent), and onsite renewable generation typically provided by rooftop photovoltaics (33 per cent).
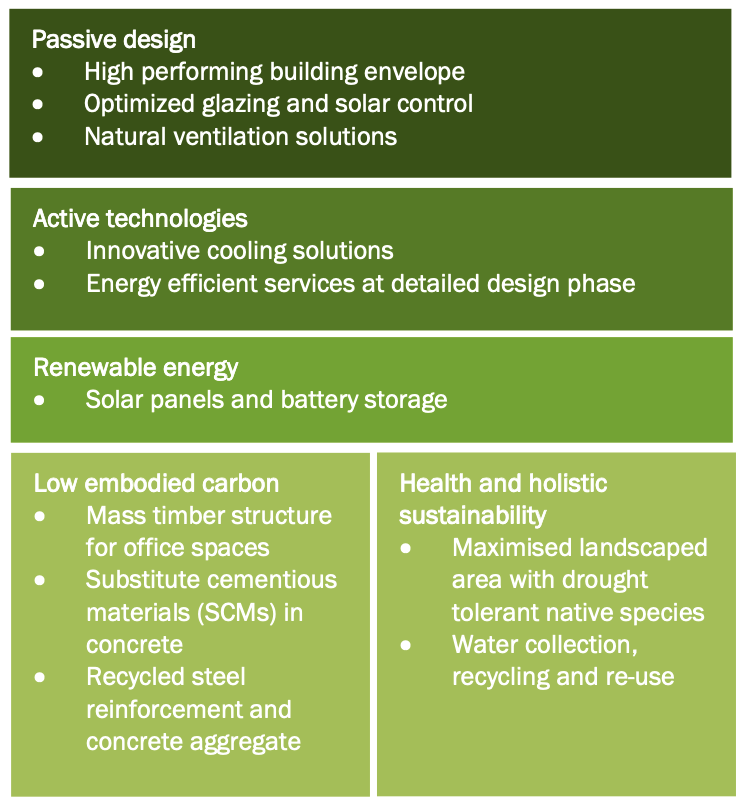
Low–carbon design hierarchy (compliments Atelier Ten feasibility vetting report)
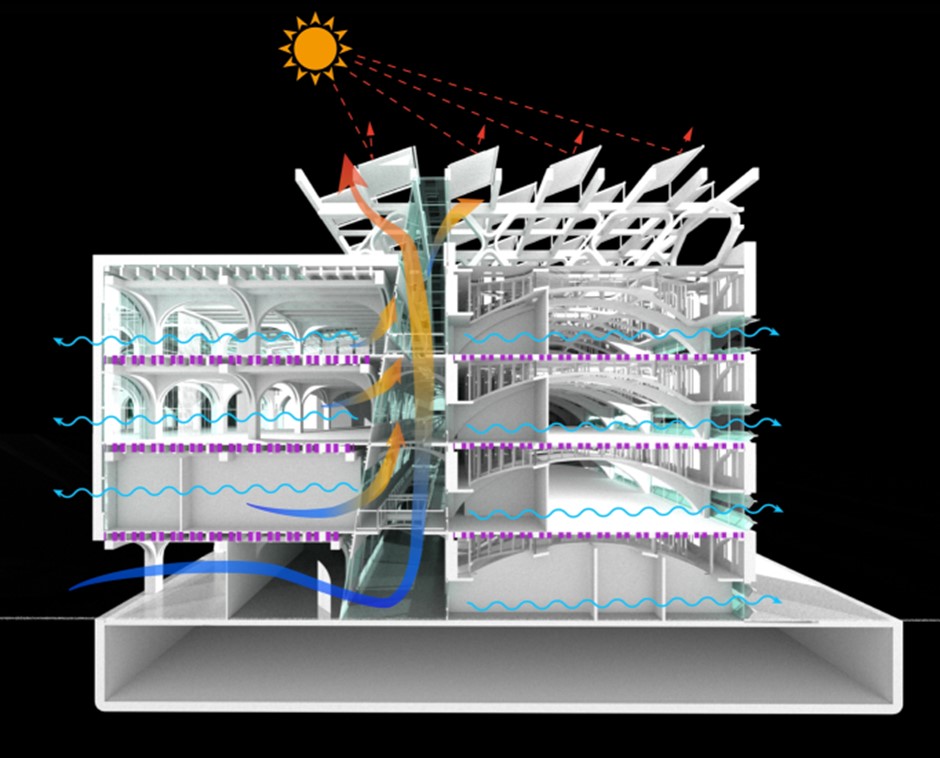
An example of student work by Frank Guo.
“With future developments in equipment technology and further detailed analysis of these energy demands, a net-zero energy laboratory may be feasible”
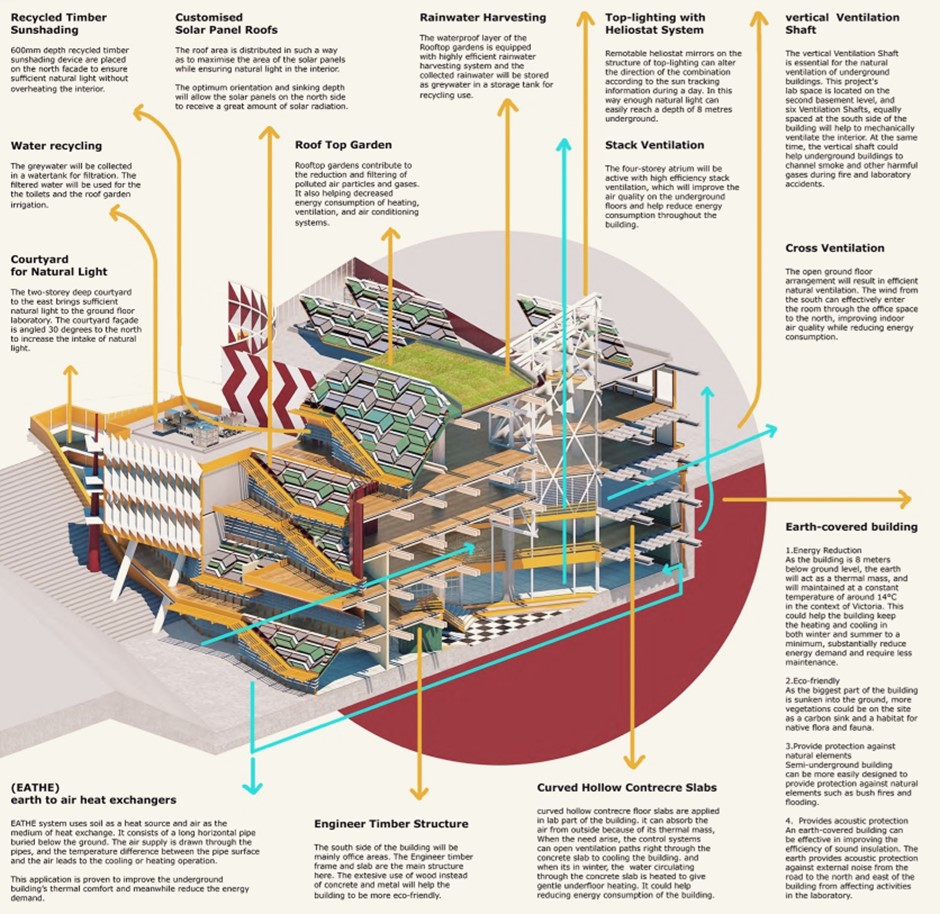
An example of student work, sustainability initiatives by Zirui Wang.
Some of the systems and technological approaches adopted in designs were:
- Passive principles for solar heating and summer control, natural ventilation, and use of daylight.
- Façade optimisation (transparency ratio) and building envelope performance.
- Innovative heat pump and insulation solutions. (Including ground sourced heat, earth insulation, and evaporative cooling solutions.)
- Photovoltaic panels.
- Timber construction (where appropriate).
- Roof-top and ground-level landscaping including water capture/treatment.
The energy demands and specific functional requirements of laboratory equipment were included in the total energy demand of the building but not considered in the energy-use reduction pathway. With future developments in equipment technology and further detailed analysis of these energy demands, a net-zero energy laboratory may be feasible.
Right now, based on the estimated reduced demand on grid energy, net zero operation carbon is possible through off-site renewable energy generation, for example through a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA).
Extending the scope of “net zero” to embodied carbon in materials, the students’ schemes were also interrogated against business-as-usual structural systems. This showed up to 35 per cent reductions in upfront embodied carbon were able to be achieved through use of timber and low-carbon concrete (cement-replacement) structural systems.
Many of the designs employed a different structural system for laboratory spaces relative to the rest of the building, recognising the more onerous vibration control requirements that exist for laboratory floors.
“The premise of the studios was to marry architecture and engineering more closely together at the early design stage”
Health and well-being
One of the principal tenets of integrated design is to include as many discipline and stakeholder representatives in the early design process as possible. This is done with the aim of generating designs and including building elements that serve as many end functions as possible at the one time. Many of the strategies adopted not only contributed to low environmental impact and carbon savings but were also chosen because they had positive impacts on occupant health, well-being and productivity.
The final outcomes that were developed represented a step forward to more informed laboratory building designs. They simultaneously reduce energy use and carbon footprint while providing a healthy and enjoyable place in which to work.

Like to know more?
For more information on i-Hub, go to www.ihub.org.au
To see Professors Brendon McNiven and Lu Aye, F.AIRAH in a video about the Integrated Design Studios, visit this link.
Like to hear more?
To hear contributor Bohemia Hookham discuss a new Passivhaus project, visit this link.