Emergency!
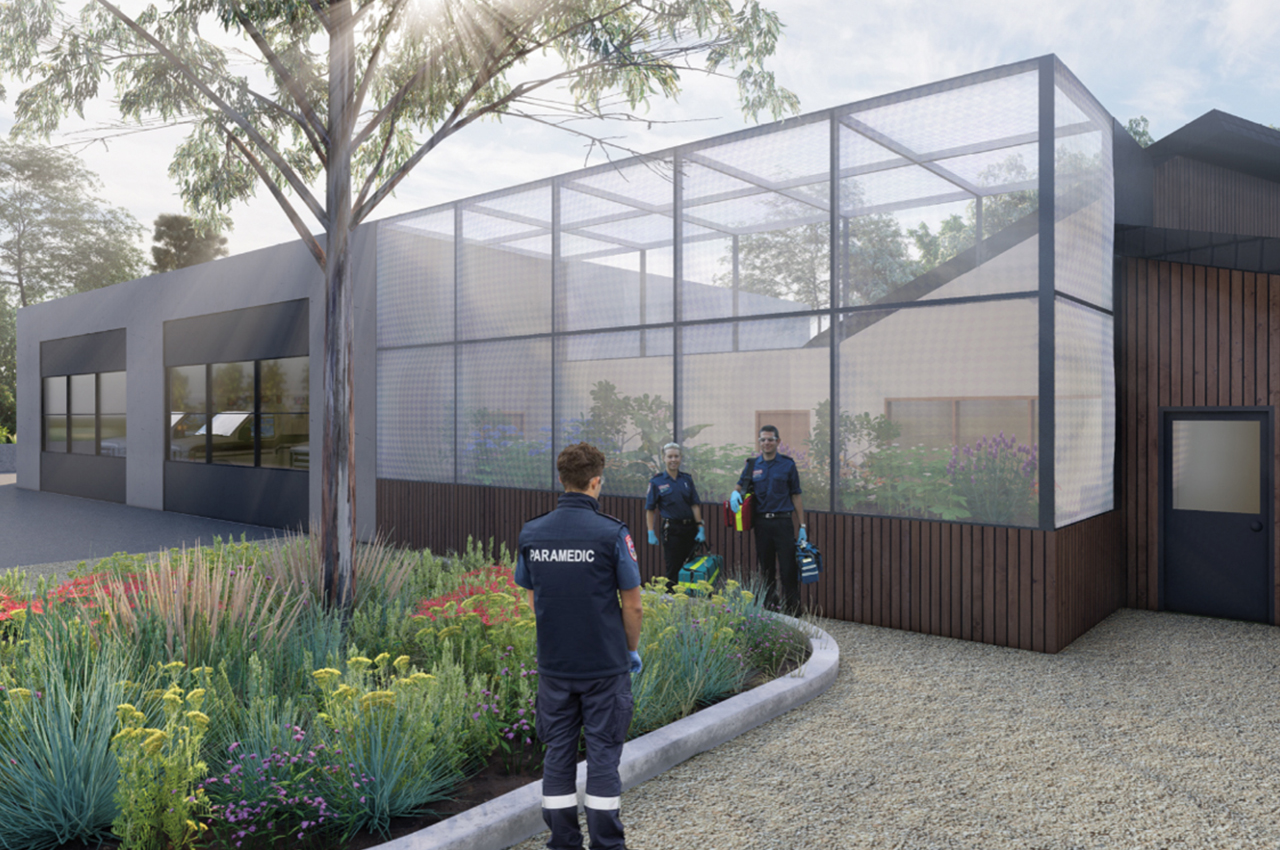

As part of the i-Hub project, masters-level architectural and engineering students from the University of Melbourne, industry consultants, university academics, and Ambulance Victoria staff embraced the challenge of designing net zero emergency response stations. The university’s Brendon McNiven; Lu Aye, F.AIRAH; and Dominik Holzer discuss.
Ambulance Victoria maintains more than 300 facilities across Victoria servicing an area of more than 227,000km². The organisation’s top priority is the health and care of the more than 5.8 million Victorians who rely on the service in times of personal emergency.
As a community-based institution, it is also highly motivated to care for the environment in which it operates. This includes the energy and carbon impacts of operations. Like many other government organisations, and in line with the Victorian Climate Change Act (2017), Ambulance Victoria is targeting zero-net carbon as an organisation by 2045.
A key part of the roadmap to achieve this is improving the performance of the ambulance stations out of which the organisation operates. In 2021 Ambulance Victoria approached AIRAH and i-Hub (the Innovation Hub for Affordable Heating and Cooling) for assistance in studying how this might best be achieved. With the assistance of masters-level architectural and engineering students from the University of Melbourne, selected consultants from industry, university academics, and Ambulance Victoria staff the challenge of designing net zero emergency response stations was undertaken.
The study took place as a part of the integrated design studios (IDSs) being carried out under the i-Hub. The studios explore how to better marry architecture and engineering to deliver building outcomes that exceed what each discipline would have been able to deliver on its own. The aim is to provide exceptional technical performance at the same time as superior architectural amenity.
The basis of integrated design is to involve all stakeholders in the design from the outset. Designs come from a holistic basis of not only servicing primary response functions, but also of being socially responsible, looking after the wellbeing of the paramedics being sent out onto the road, and serving ancillary functions such as community gardens or providing safe places of refuge for the community in times of need.
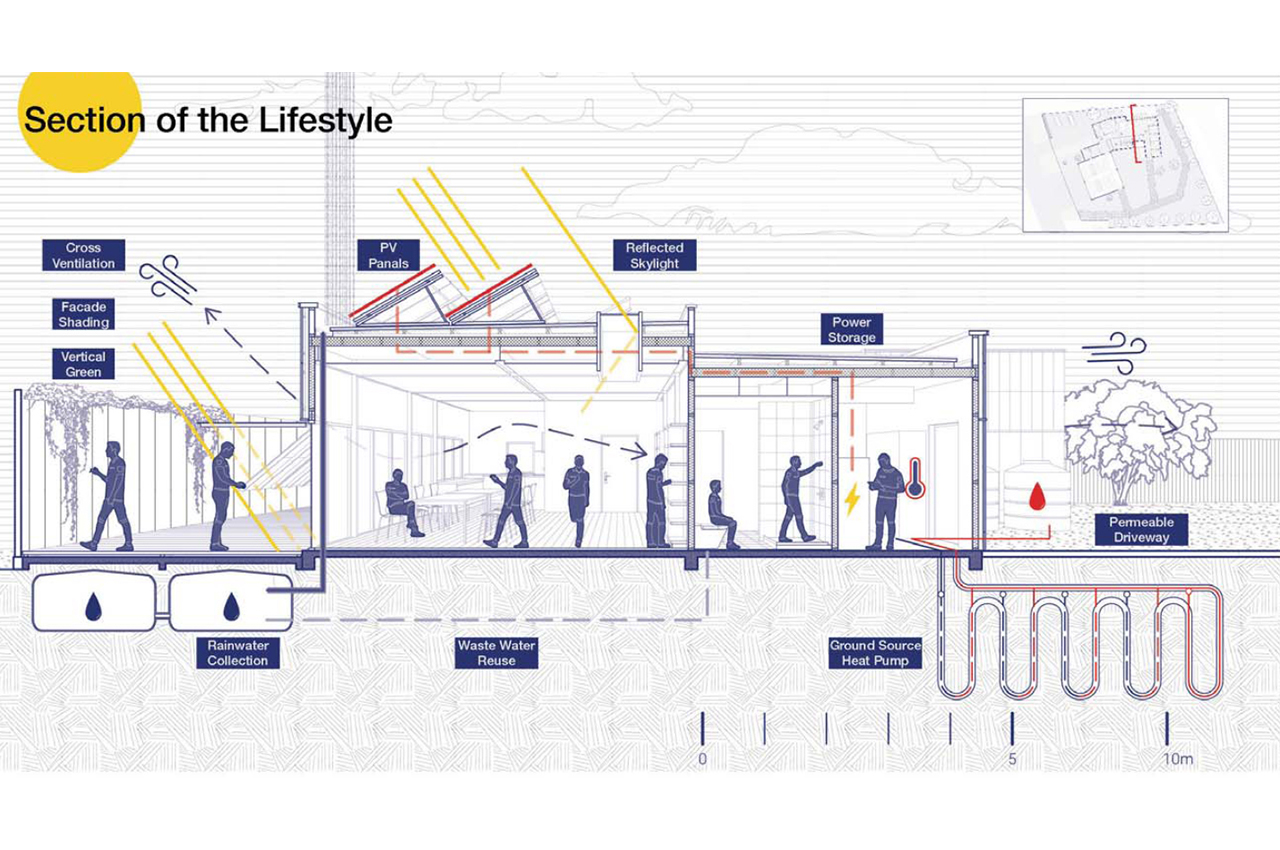

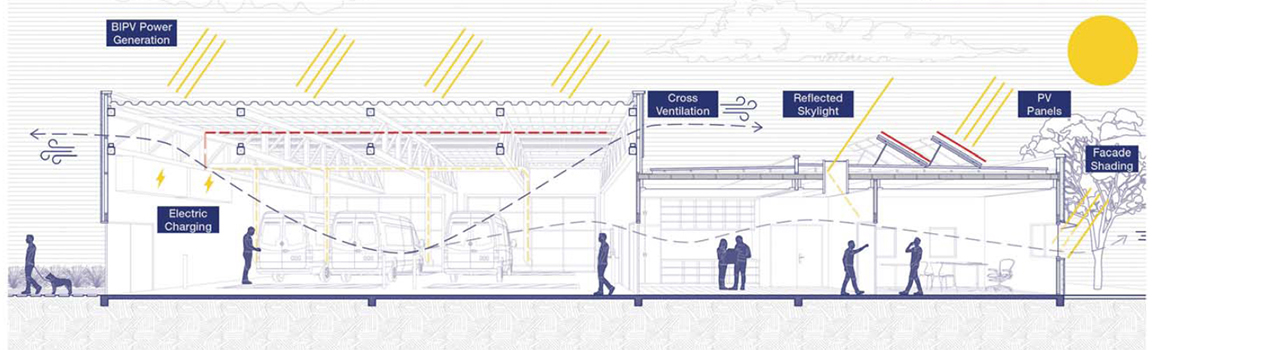

Readily achievable solutions
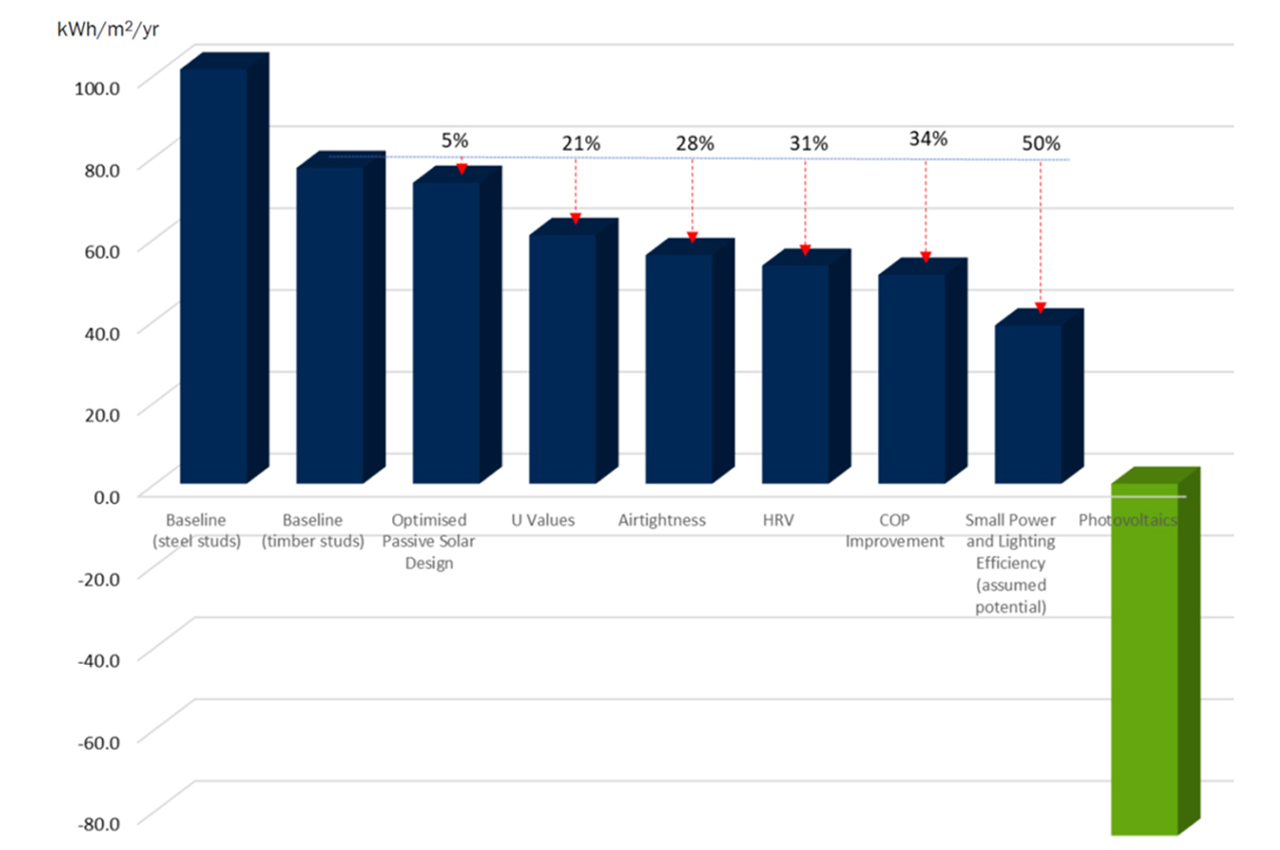
The body of work produced demonstrated that cumulative savings of up to 50 per cent in operational energy compared to business as usual could be achieved. Building from this lower demand base, the study went on to show the potential energy able to be generated through the use of onsite renewables (i.e., photovoltaics), was significantly more than the building uses on an annual basis, thus achieving net zero operational carbon impact.
The technologies and systems proposed were taken from tried-and-tested solutions in Australia able to be readily adopted for this scale of the project.
The key systems offering greatest benefit are:
- Optimised passive solar principles for winter heating and summer control.
- High-performance building fabric through enhanced U-values of the building fabric.
- Reduction in thermal bridging and airtightness construction quality assurance.
- Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery providing energy savings in addition to indoor environmental quality and health benefits.
- Photovoltaic panels were consistently applied across projects for onsite renewable energy generation.
“The study went on to show the potential energy able to be generated through the use of onsite renewables … was significantly more than the building uses on an annual basis”.
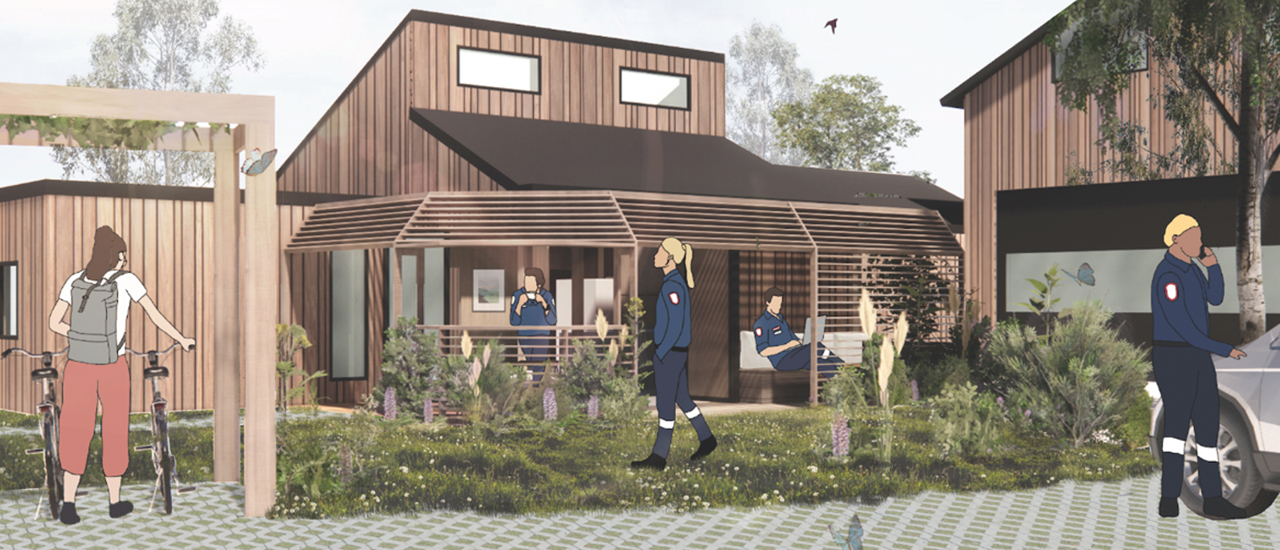


Enhanced life-cycle benefits
Calculations on the energy and running cost savings showed that all of the technologies identified above yield a net beneficial economic payback over the life of the asset, providing a compelling business case for their incorporation into future station designs.
Enhanced health outcomes
In addition to the financial business case, the measures also offer health and wellness benefits that are a significant value-add to end-users of the ambulance station. Good daylighting in spaces, access to the sun, thermal comfort and well-designed ventilation systems are key indoor environmental amenity outcomes that benefit through staff well-being and reduced sickness rates.
While natural ventilation is applicable for a large part of the year on most sites, the use of heat-recovery ventilation in winter is of particular note as a means of achieving healthy internal air quality and minimising energy use.
As well as learnings on appropriate net zero design technologies, Ambulance Victoria raised its own internal capability and understanding of what is involved in delivering sustainable buildings. The learnings gained enable the organisation to speak out and have more influence in the design of the facilities out of which it operates.
“The use of heat-recovery ventilation in winter is of particular note as a means of achieving healthy internal air quality.”

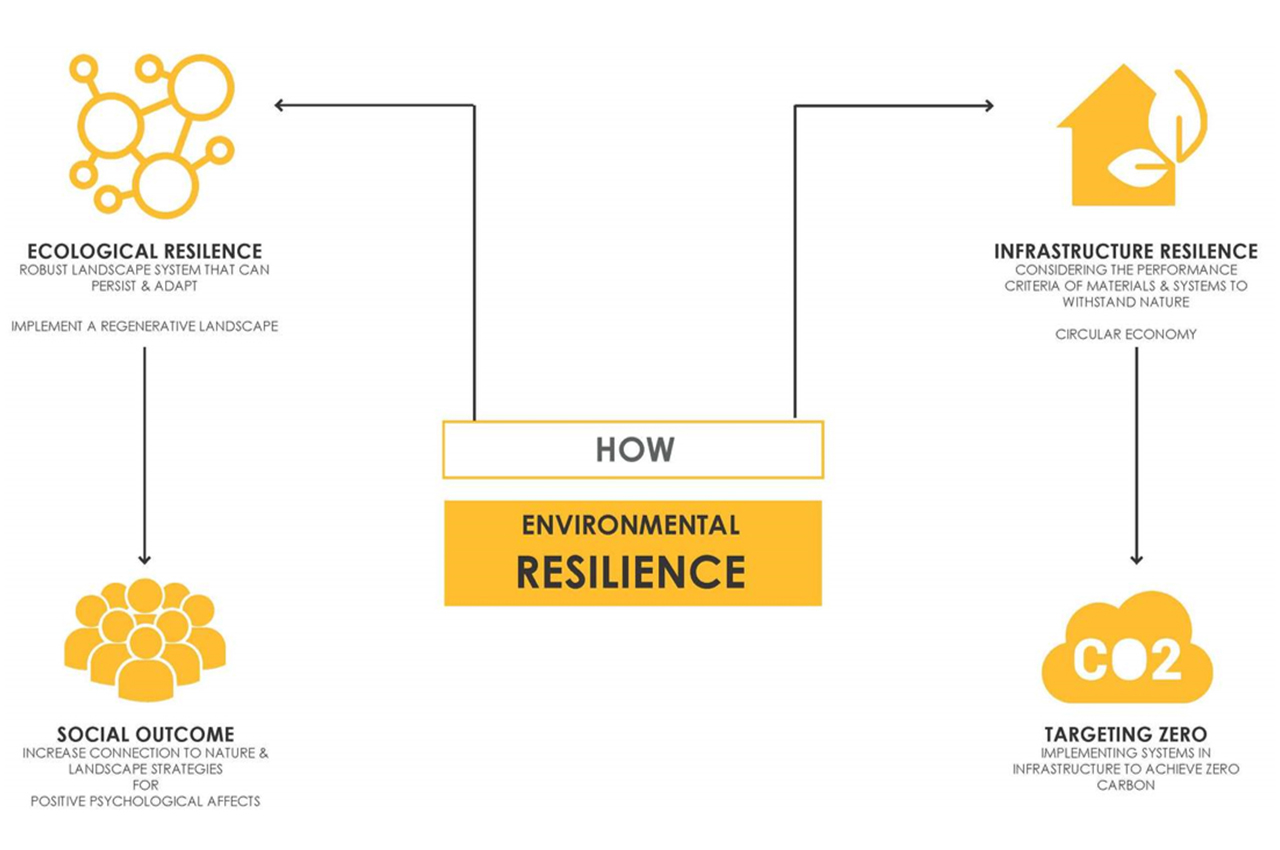

The future
The net zero future is bright for Ambulance Victoria. The organisation has already taken the lessons learned in the Integrated Design Studio and used them to inform internal policy around the development of future stations. The first of these will be a new net zero prototype station currently under planning for Mallacoota. On this build it hopes to explore volumetric modular design to harness quality and thermal performance.
Further energy challenges no doubt await as it begins a transition to zero emission vehicles.
This project received funding from ARENA as part of ARENA’s Advancing Renewables Program

This article appears in Ecolibrium’s October 2022 edition
View the archive of previous editions
Latest edition
See everything from the latest edition of Ecolibrium, AIRAH’s official journal.




